Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the way many devices work. They’re not just doing tasks; they’re learning from what happens around them, adjusting to new situations, and even predicting what might happen next. Businesses are starting to use these new opportunities.
Here’s What’s Happening:
- AI software development is increasingly focusing on applications for on-site hardware, moving beyond centralized data centers.
- A significant trend in chip manufacturing is the integration of AI capabilities directly into hardware components.
- There’s a surge in the development of AI chips, uniquely designed to execute complex operations with astonishingly low power consumption – sometimes only a few microwatts.
- Various sectors, including logistics, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and healthcare, are witnessing the introduction of machines equipped with AI.
- Stats suggest a significant surge in AI-embedded device shipments, growing from 79 million to an estimated 1.2 billion in 2023.
- The progression from data centers to on-device AI is being propelled by advancements in both software and hardware technologies. For instance, the advent of processors capable of efficiently running machine learning algorithms while conserving energy is crucial for mobile devices. This technological leap is evident in the increasing investment in AI chip development companies, with funding surpassing US$1.5 billion recently, reflecting a notable increase from previous years.
- Innovations in AI chips are noteworthy. A recent development from MIT researchers showcases a chip capable of executing neural network computations up to seven times faster than its predecessors, while consuming up to 95% less energy. This efficiency makes such chips ideal for deployment in Internet of Things (IoT) devices, including sensors that operate on low power.
- Smartphones and similar devices are increasingly incorporating AI chips, with predictions indicating over half a billion such devices will feature machine learning capabilities. Continued advancements in AI hardware and software are expected to expand the range of devices with integrated AI functionalities. Research indicates that by 2023, approximately 43% of AI analysis will occur at the edge of networks, marking a significant shift from centralized data processing.
Overall, AI’s trajectory is not just about enhanced capabilities; it’s about the widespread integration of intelligence across a spectrum of devices, both for consumer and enterprise use. This evolution is setting the stage for an era where pervasive intelligence becomes a defining characteristic of technology.
The Rise of Autonomous Smart Devices and Edge Computing
In the forthcoming landscape, we will witness a surge in AI-infused smart devices capable of discerning and responding to visual, auditory, and pattern-based stimuli. These devices will evolve through experiential learning, adapt dynamically to fluctuations in their environment, and forecast potential outcomes. A significant feature of these devices will be their ability to intuit user requirements and preferences, as well as to engage in collaborative efforts with other devices through data exchange, task allocation, and coordinated actions.
A key aspect of this evolution is the integration of AI directly into these devices, as opposed to their reliance solely on cloud-based intelligence. This decentralization means that these devices’ functionality won’t be hindered by internet connectivity issues. Additionally, by processing data locally, they avoid the delays associated with sending information to the cloud for analysis. This reduction in latency, coupled with the independence from constant connectivity, opens up possibilities for a multitude of applications, such as in-vehicle navigation systems, augmented reality experiences, and certain medical applications, all requiring immediate response and consistent performance, irrespective of connectivity strength.
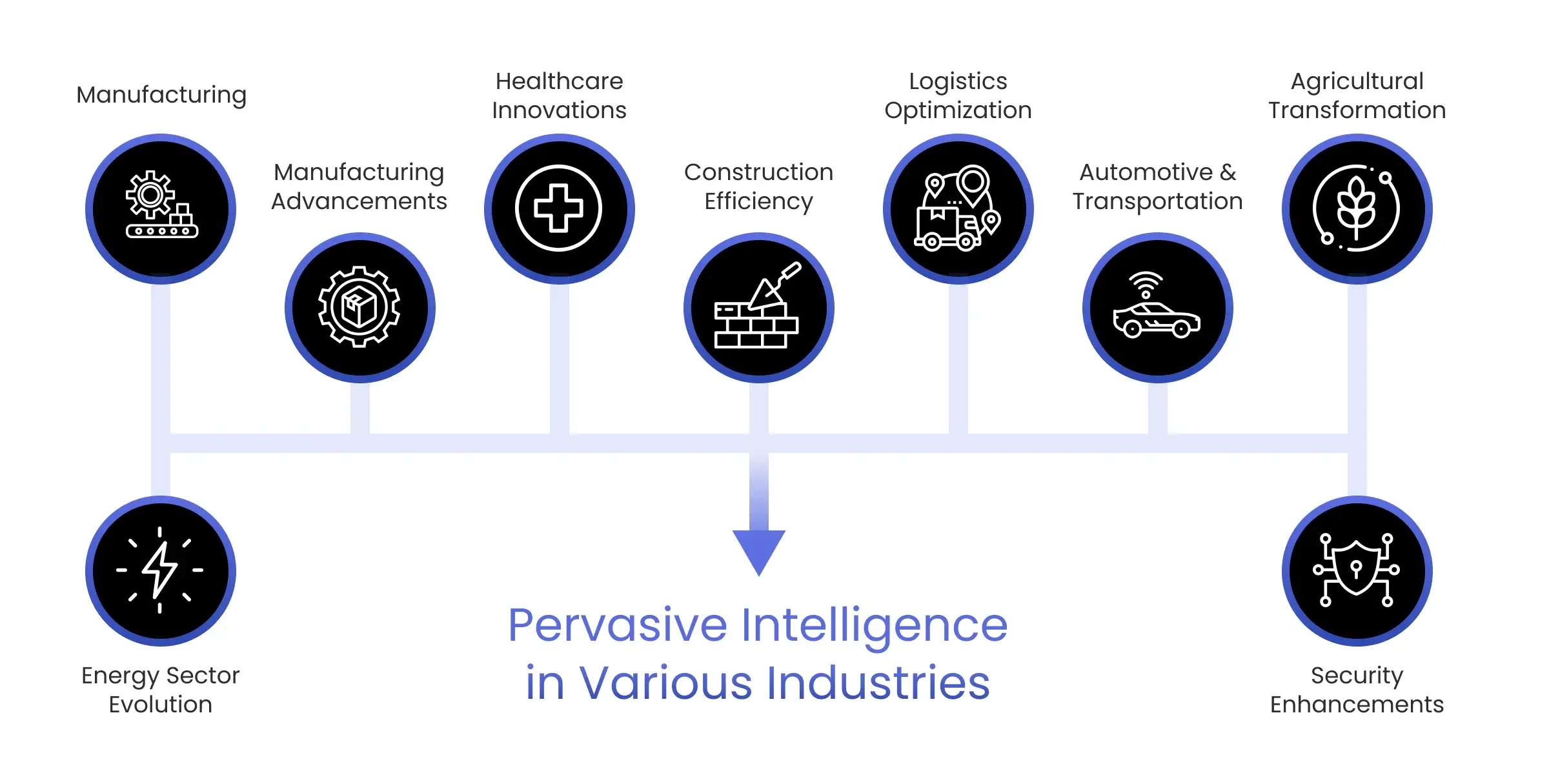
Pervasive Intelligence in Various Industries
This wave of pervasive intelligence is poised to revolutionize various industries, bringing enhancements to not only operational processes but also potentially altering the dynamics within these sectors.
1. Manufacturing
The introduction of AI and sensory technology into robots has revolutionized their utility in manufacturing environments. These ‘cobots’ (collaborative robots) are now able to work safely and efficiently alongside human workers. Through advancements in embedded computing, these robots can now process tasks at unprecedented speeds, ensuring continuous production and reducing downtime.
2. Manufacturing Advancements
Beyond robots, other manufacturing equipment can benefit from on-site intelligence. For instance, AI-empowered smart valves can minimize chemical leakages and operational interruptions.
3. Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, AI-enabled medical devices are transforming patient care, making it more cost-effective and enhancing patient outcomes. Trials with AI-embedded implants for epilepsy have shown promising reductions in seizure frequency. These advancements hint at a future where remote monitoring and treatment become the norm, offering significant cost savings.
4. Construction Efficiency
AI applications in construction, like drone-based site monitoring and smart cameras, aim to reduce delays and material waste. Innovations in autonomous inspection vehicles have already demonstrated substantial improvements in productivity and budget management.
5. Logistics Optimization
In the logistics sector, intelligent robots are redefining efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The integration of AI across cloud and local data centers enables these robots to collaboratively expedite order fulfillment, markedly reducing processing times.
6. Automotive and Transportation
The advent of autonomous vehicles signifies a major shift in transportation, potentially reducing the need for personal vehicle ownership and reshaping urban infrastructure and various business models, including insurance and logistics.
7. Agricultural Transformation
In agriculture, robotic technology like AI-guided herbicide sprayers is significantly reducing chemical usage and operational costs, showcasing a move towards more sustainable practices.
8. Energy Sector Evolution
The energy industry, particularly in wind farming, is benefitting from networked turbines with embedded sensors and algorithms, enhancing power generation efficiency and reducing equipment wear and tear.
9. Security Enhancements
In the security domain, AI-powered smart cameras are set to revolutionize surveillance capabilities, enabling real-time identification and response to potential security threats.
These developments signify a profound shift towards a world where AI is not just a cloud-based phenomenon but an integral, pervasive part of our daily lives and industrial operations.
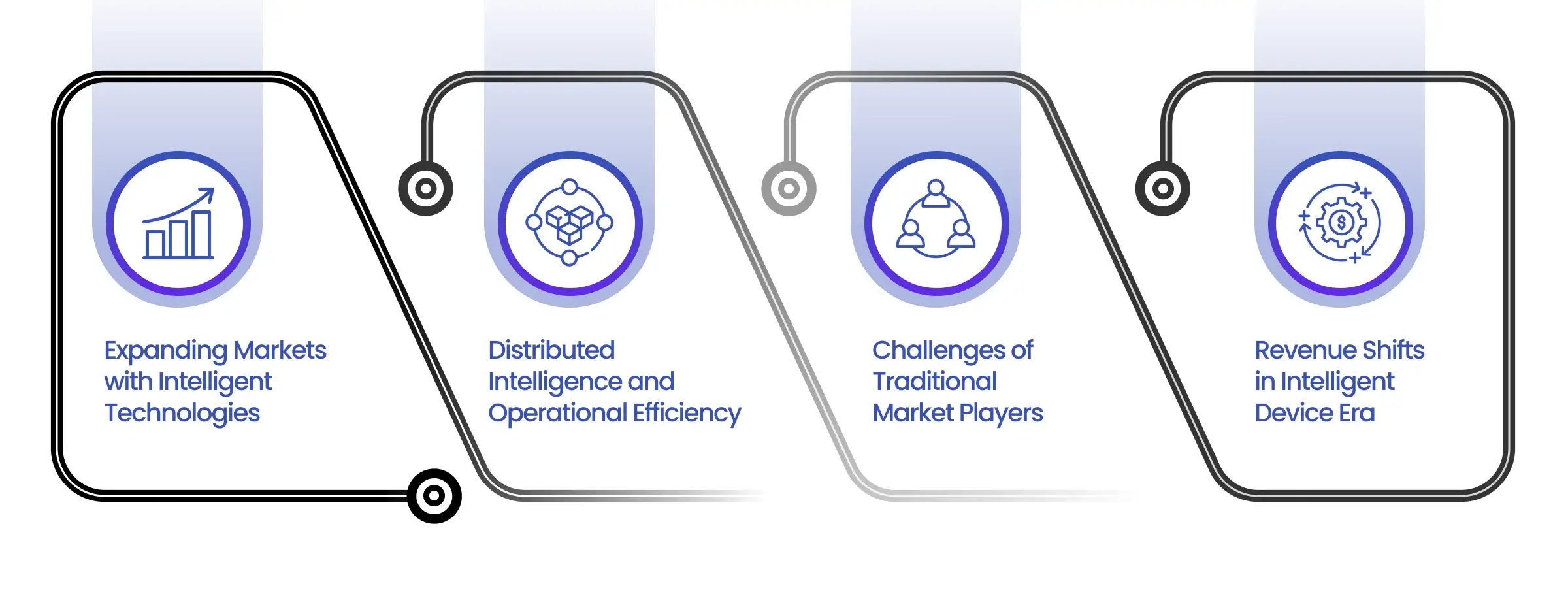
Benefits of Pervasive Intelligence
In the business world, intelligent technologies offer significant transformative potential. These innovations enhance operations and create new market opportunities. This discussion focuses on how intelligent systems can impact efficiency, market growth, competitive landscapes, and revenue distribution.
1. Expanding Markets with Intelligent Technologies
Advanced technologies like AI-driven warehouse robots revolutionize industry efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For example, these robots in online grocery logistics can speed up order processing and delivery. This reduces major barriers to online grocery shopping. In renewable energy, smart wind turbines using collective intelligence make wind energy more cost-competitive, increasing demand in various regions. In surveillance, AI-enabled cameras capable of autonomous analysis extend their use to areas where continuous human monitoring is unfeasible.
2. Distributed Intelligence and Operational Efficiency
Swarm intelligence, where interconnected intelligent systems collaborate, is emerging in various sectors. This collective decision-making enhances speed and efficiency. A prime example is AI-integrated traffic systems, which in Pittsburgh reduced travel and idling times by optimizing traffic flow through real-time data analysis and signal communication. Similar distributed, cooperative systems are being explored in agriculture, infrastructure, and security.
3. Challenges of Traditional Market Players
Companies producing conventional products are challenged by new smart technology alternatives. Consumer preferences are shifting towards intelligent solutions in industries like surveillance and agriculture. To stay competitive, these companies need to incorporate smart technologies into their product lines. The automotive industry’s investment in autonomous vehicle technology is a notable example. Other sectors should similarly focus on strategic partnerships and acquisitions to integrate AI into their products.
4. Revenue Shifts in Intelligent Device Era
Intelligent devices are redefining industry revenue models. In the automotive sector, autonomous ride-hailing services may reduce personal car ownership, shifting revenue to fleet operators. When it comes to agriculture, smart technologies like robotic herbicide sprayers could decrease chemical reliance, impacting the global herbicide and fertilizer markets. In healthcare, AI-based medical devices, like epilepsy management tools, could shift spending from emergency care to technological treatments, offering significant cost savings for patients and insurers.
Overall, pervasive intelligence in business not only boosts operational efficiency but also opens up market expansion, challenges existing players, and realigns revenue streams. Businesses must adapt and innovate to leverage the opportunities presented by this intelligent evolution.
Implications on Business
In the forthcoming phase of widespread intelligence, leaders in business and technology will encounter both prospects and challenges in various roles.
- For those overseeing operations, the focus shifts to selecting, integrating, and utilizing intelligent products, enhancing organizational speed and efficiency. The realm of product marketing is evolving, necessitating strategies for the next wave of intelligent products. A case in point is the smartphone industry, where manufacturers are embedding AI capabilities like image and speech recognition that operate independently of cloud connectivity. An example is a smartphone that aids users in photography by capturing numerous shots rapidly and suggesting the optimal ones. These advancements, including augmented and virtual reality, will also facilitate personalized experiences based on machine learning of user preferences. Predictions by Gartner indicate that in 2023, 80% of smartphones shipped possess embedded AI, a significant increase from the previous year.
- Market strategists need to grasp how intelligent devices could alter industry dynamics. When embedded intelligence can enhance products or service delivery, it’s crucial to identify opportunities for increased market value or product differentiation. This is particularly relevant for manufacturers of goods like pesticides or construction materials, which might see a decline in demand if customers adopt smarter, more efficient processes.
- Strategists must also explore how widespread intelligence can spawn new revenue streams and business models. Examples include telecom operators integrating computing infrastructure into cellular base stations for data analysis services or as a managed service. Manufacturers can exploit the adaptability of collaborative robots for rapid production of customized items, while media companies might leverage on-device AI for premium, personalized services or augmented reality experiences.
- Risk management leaders are tasked with collaborating with product marketers to evaluate potential risks of new products, particularly those used in sensitive environments such as vehicles, personal spaces, or human bodies. Addressing risks related to algorithm bias, decision accuracy, data privacy, and cybersecurity is imperative. This requires a blend of technical and operational strategies, keeping in mind the ethical considerations, especially when individual rights are at stake.
(Also read about LLM application).
Future of Pervasive Intelligence
The pervasive intelligence era is on the horizon, although its significant impact on industries might take years. The future promises devices with embedded intelligence becoming commonplace in commercial and personal environments, ushering in new levels of performance and efficiency. Therefore, companies must strategize now to understand the potential influence of pervasive intelligence on their business and industry, positioning themselves to capitalize on its benefits.
Pervasive Intelligence Vs. Artificial Intelligence
Aspect |
Pervasive Intelligence |
Artificial Intelligence |
| Definition | A broad concept that involves true collaboration between tools and systems, integrating human experience and AI results. It spans the entire lifecycle of a process or system, leveraging all available forms of intelligence. | A branch of computer science focused on creating systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. |
| Scope | Encompasses the entire process or lifecycle, integrating various tools and steps, and focusing on collaboration and data sharing. | Often limited to specific tasks or applications within a system, without necessarily integrating with other processes or the overall lifecycle. |
| Human Element | Actively incorporates human expertise and experience, blending it with AI capabilities for enhanced outcomes. | Generally focuses on automating tasks without explicit integration of human experience, except for initial programming and learning phases. |
| Application | Used in complex systems like Electronic Design Automation (EDA), where multiple tools and steps are interconnected, sharing data and insights. | Applied in a wide range of fields from simple applications like voice recognition to complex systems like autonomous vehicles. |
| Collaboration | Requires a high level of integration and collaboration between different tools and stages in a process. | May function independently or as part of a larger system, but doesn’t inherently require collaboration between different AI systems. |
| Intelligence Source | Leverages both AI-generated insights and human expertise, creating a more holistic approach to problem-solving. | Relies primarily on data-driven insights and machine learning algorithms, with less emphasis on human-derived intelligence. |
| Lifecycle Integration | Integral to the entire lifecycle of a process, from design to implementation and optimization. | Often focused on specific phases of a process, such as initial design or problem-solving, without ongoing integration throughout the lifecycle. |
| Goal | Aims to create a synergistic environment where AI and human intelligence coexist and enhance each other, leading to more efficient and effective processes. | Seeks to automate tasks and solve complex problems using AI algorithms, primarily aiming at efficiency and accuracy. |
Advancing Business Operations with Pervasive Intelligence
Pervasive Intelligence stands at the forefront of reengineering business processes and product development in the enterprise landscape. This paradigm shift from traditional methodologies to a more data-driven, AI-infused approach yields transformative benefits. A detailed examination of these benefits reveals:
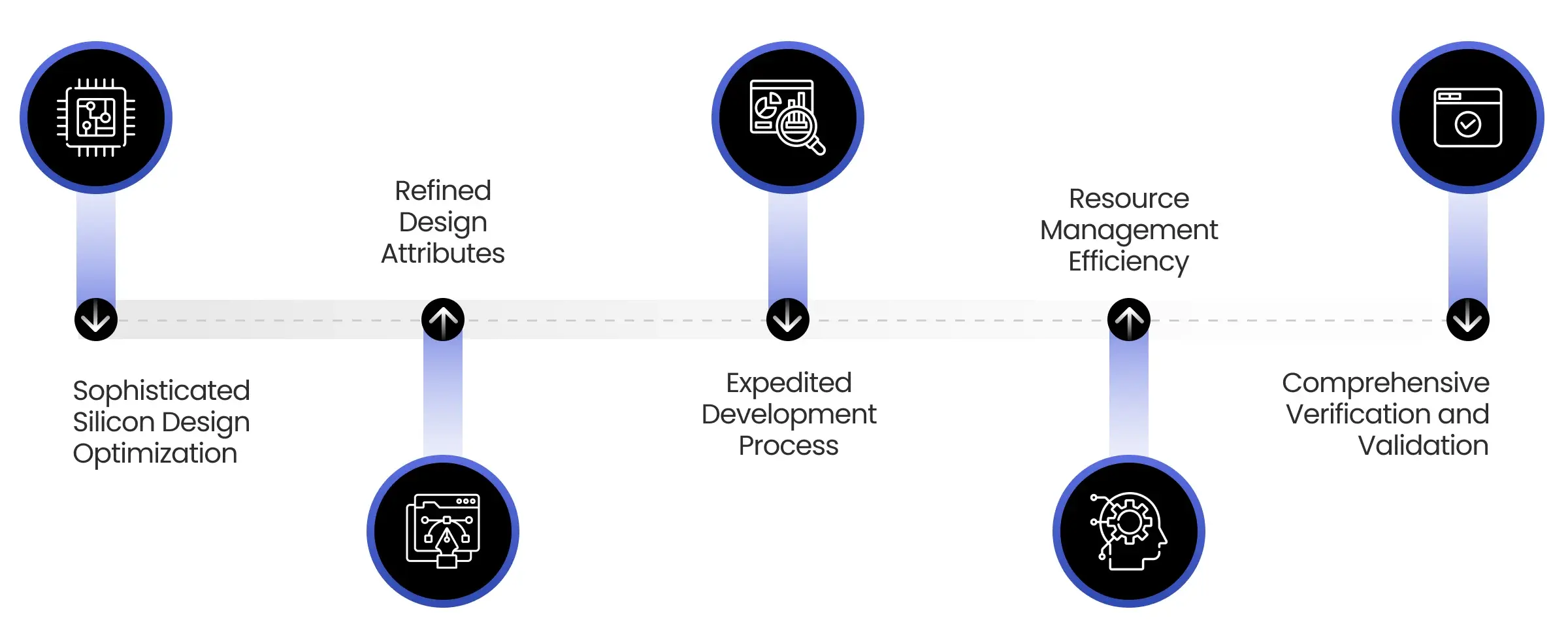
1. Sophisticated Silicon Design Optimization
Through Pervasive Intelligence, enterprises can significantly enhance silicon chip architecture. This goes beyond the conventional Power, Performance, and Area (PPA) metrics. It involves intricate calibration of chip design to achieve higher processing speeds, minimal footprint, and optimized power consumption, aligning with the demands of modern technology.
2. Refined Design Attributes
Pervasive Intelligence extends its influence beyond PPA metrics to refine other critical aspects of silicon design. This includes improving manufacturability – reducing complexities in production processes, enhancing functional safety – ensuring reliability under diverse operational conditions, and bolstering security measures against increasing cyber threats.
3. Expedited Development Process
In today’s fast-paced market, time to market (TTM) is crucial. Pervasive Intelligence streamlines the development cycle, enabling businesses to swiftly navigate from conceptualization to market launch. This rapid development process is vital for gaining a competitive edge and capturing market opportunities effectively.
4. Resource Management Efficiency
By integrating Pervasive Intelligence, enterprises can optimize the allocation and utilization of both human talent and computational resources. This strategic resource management leads to cost-efficient project development, maximizing profitability and resource sustainability.
5. Comprehensive Verification and Validation
The implementation of Pervasive Intelligence ensures a more rigorous and thorough approach to verification, validation, and sign off processes. This reduces the need for subsequent modifications or ‘chip turns,’ thereby avoiding delays and additional costs that can impact the overall project timeline and budget.
In essence, Pervasive Intelligence is reshaping the way businesses approach operational efficiency, product innovation, and market competitiveness. Its detailed application across various facets of enterprise operations marks a significant leap towards more intelligent, efficient, and effective business practices.
Key Solutions Offered by Markovate
- Real-Time Performance Analytics: Custom solutions that track and analyze business operations, offering insights for continual improvement.
- Intelligent Customer Interaction Systems: Tools that provide a personalized customer experience based on behavior and preferences.
- Automated Process Optimization: Solutions that streamline and automate key business processes, enhancing efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance Systems: AI-driven tools that predict equipment maintenance needs, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Smart Supply Chain Management: Systems that optimize supply chain operations using real-time data and predictive analytics.
- Custom AI-Driven Business Solutions: Bespoke solutions addressing unique challenges and objectives of each business.
Choosing Markovate means partnering with a team that deeply understands your business challenges and opportunities. We collaborate closely to ensure our solutions are not just technologically advanced but also aligned with your strategic goals. Connect with the Markovate team today to explore how pervasive intelligence can transform your business.
FAQs
1. What is Pervasive Intelligence and How Can It Benefit My Business?
Pervasive Intelligence refers to the integration of intelligent, connected technologies across your business operations. It benefits your business by enhancing data-driven decision-making, increasing operational efficiency, improving customer experiences, and providing a competitive edge through adaptive strategies.
2. How Does Pervasive Intelligence Improve Decision-Making in Business?
Pervasive Intelligence improves decision-making by providing real-time data and advanced analytics. This leads to more accurate and timely decisions, allowing your business to respond quickly to market changes and customer needs.
3. Can Pervasive Intelligence Be Tailored to Specific Industry Needs?
Absolutely. Pervasive Intelligence solutions can be customized to address the unique challenges and requirements of different industries. This ensures that the solutions are not only technologically advanced but also relevant and effective in your specific business context.
4. What Are the Key Considerations When Implementing Pervasive Intelligence in a Business?
Key considerations include identifying specific business needs, ensuring data security and privacy, choosing the right technology partners, and planning for seamless integration with existing systems. Additionally, employee training and change management are crucial for successful implementation.
5. How Does Pervasive Intelligence Impact Customer Experience?
Pervasive Intelligence significantly enhances customer experience by enabling personalized interactions based on intelligent insights into customer behaviors and preferences. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, better business outcomes.