Last Updated on 29-Jan-2021
Marketers will likely be familiar with on-page SEO best practices: intent-based optimization, fast-loading web pages, interlinking, and more. But how many apply these practices to their site?
Reading about the best practices is one thing, but executing them is another hurdle altogether. If you’re one of the people stuck on how to implement the on-page SEO best practices you’ve been reading about, stick around for our actionable tips.
Today we’re going to breakdown the top on-page SEO best practices. You’ll learn why they are considered essential to an SEO marketer’s toolkit, and the many ways you can implement them for higher rankings on SERPs.
Intent-Based Optimization
Google’s ultimate goal is to satisfy a user’s search intent.
Knowing that this is Google’s intent, it makes sense that the content on your website should work toward the same goal as well.
Intent-based optimization is identifying the main needs and concerns that users are looking for when they search for a specific term and addressing those needs in your content.
In general, there are three different types of intent:
Informational intent is when the searcher is looking for a solution. They commonly use questions such as “What is ____?”, “How does ____ work?”, and “How do I use ____?”
Commercial/Transactional intent is when the user wants to buy a product. They will typically use queries such as “Best (product name)”, “(Product name) reviews,” and “(Product name) vs (competitor).”
Navigational intent is when a user is seeking a specific website and will type that query into their search bar. The only way to get to this level of intent is through brand awareness and building your online community.
Why is intent-based optimization important?
The success of your marketing largely depends on the intent behind your keywords. Targeting your campaigns for the wrong intent can waste a lot of your budget fast. With PPC ads, for example, you pay for each click, so if those clicks don’t lead to qualified leads, you’re wasting money.
It’s not just your on-page SEO that will benefit from intent-based optimization. Having a customer-centric approach to your content will fulfill their needs and affect your conversions.
How do I optimize my page for intent-based queries?
The first thing you’ll want to do is research some keywords related to your business offerings. In the search results, you are looking for two things: ads from similar companies and blog posts.
If ads pop up, that’s a good sign, as it means other companies think this is a good intent-based keyword. You’ll have more competition, but the customer intent is there, so all you have to do is have a better copy or a more unique selling point.
If you see a variety of blog posts, forums, or discussion topics about your services, that’s also a good sign. This means people are actively looking for a solution, and you’ve found an opportunity and a place to direct them to your website.
Above all, you want to give customers the experience they are looking for when visiting your site. If you have the solution, show it to the people who are actively searching, and this will lead to more conversions.
Fast Loading Web Pages
Everyone wants a faster loading web page, but how long are customers willing to wait for a page to load? Google says you should aim for 3 seconds, but 47% of consumers expect websites to load in two seconds or less. And around 40% will abandon a page that takes three or more seconds to load. Beyond not wanting to have your customers wait, Google also ranks sites based on your page speed. Therefore it is in the best interest of your customers and your on-page SEO campaign to have a faster loading page. Finding a good hosting for fast loading website can be a challenge, but using an article written by Who is hosting will enable you to find a hostings company that will work to meet your needs within your budget.
Why is this important?
A slow web page impacts everything from sales to conversions and user engagement. Because page speed is included in Google’s ranking, load time can influence how easy it is for customers to find your page in the first place.
Once they click on your page, even if it takes one second to load, that delay results in:
- 11% fewer page views
- 16% decrease in customer satisfaction
- 7% loss in conversions
And for a page that takes more than 3 seconds to load? You’ll lose half of your potential customers before they’ve even seen your site.
What causes pages to load slowly?
According to Yahoo, 80% of a web page’s load time is spent downloading the different parts of the page. Anything from images, scripts, and other on-page components takes longer to render. This is because an HTTP request is made for each one of these elements, so the more you have, the longer it will take to load. Thankfully there are ways to combat this.
How do I increase my web loading speed?
On the front end, you can compress your on-page elements. Reduce the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files that are larger than 150 bytes. With images, you want to compress them in Photoshop so that you can retain the quality of the image. Make them the right size and file format, such as PNGs for graphics and JPEGs for photos.
You can also optimize your code by removing spaces, commas, and other unnecessary characters. Also remove code comments, formatting, and unused code. This can increase your page speed dramatically.
Simple & Readable Content
One large component of your website that you can optimize is of course—your content!
Having content that isn’t optimized will go unnoticed by search engines, and therefore won’t be read by the masses.
What’s more, having organic content on your website versus paid ads will result in more clicks. Searchers are 8.5X more likely to click on organic results than paid ads. And content also brings 85% more traffic to websites than paid advertising services.
Although you may think of content as free to create, you will need to invest a significant amount of time and effort to make it work.
How do I optimize my content?
Make your content linkable
From a search engine’s perspective, there is no difference between the best and worst content on the web if people can’t link to it. Unlinkable content is bad in the eyes of search engines, and they are unlikely to rank it. Meaning the content you’ve worked so hard to produce won’t drive traffic to your website. Examples of unlinkable content are pages that are only accessible after logging in, and content that can’t be shared.
Use keywords
When optimizing your content, you should optimize the entire page for a single keyword. It needs to be clear to search engines and customers what your page is about, and how it is relevant to your given topic, title, and metatags.
Some of the on-page SEO features you should be optimizing are topics found in this post:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Alt tags
- Media (images, videos)
- H1, H2, and H3 tags
- Internal linking
Optimize older posts
Optimizing older posts can have an enormous impact on organic rankings. It’s best to start with the content that is ranking fairly well but needs a slight push with on-page SEO to land on the first page. Analyze the pages that are outranking you and see if they have topics that you should include in your copy. Then, expand on those subjects and offer real value to readers. This way Google will rank your page higher as well.
Although you have already devoted plenty of resources to creating content, your digital marketing services are only half complete if you let that content sit on pages 2, 3, or worse. Get your content onto the first page to reap the most rewards.
Strategic Use of Metatags
Metatags are what search engines scan on your page to make sure that the content on your site best matches user inquiries.
As we learned in the first section, search engines are learning to value a good user experience and produce results that satisfy a user’s search intent above everything else. Optimizing your metatags, mainly your title, description, H1 tags, and ALT text, helps search engines and users see what your page is about concisely. You can also use your metatags to highlight the most important elements of your business and stand out in search results.
Why are metatags important?
Metatags on each of your pages are important SEO-wise because, through your title, description, and content, you can let Google know what your website is about. In particular, you want to pay special attention to the metatags on your homepage.
All websites, whether it is a blog, corporate website, eCommerce store, need homepage optimization. Even if you do not expect to get high rankings on your homepage, often the homepage is the first page users see. If they land on a different page, they will most likely navigate back to your homepage to get a full view of what the company offers.
The homepage can also rank in top positions for competitive keywords because it absorbs all the power and rankings from the rest of your pages. This is done through interlinking, which we will talk more about later on in this post.
How do I strategically use my metatags?
Optimize the homepage title
Instead of just using the business name as the homepage title, make sure you’re using the full amount of characters at your disposal. You have 60 characters to fill with keywords and more information on the business. Show off the main focus of the business in the title, and try to put your keywords at the beginning. However, be careful not to confuse Google by placing too many keywords in the title. Only add the keywords you want to be known for.
Optimize descriptions
The description of the site is what users see on SERPs, so you’ll want to make it appealing. This is what users will base their decisions on when deciding which link to click. A text summarizer can prove beneficial in creating appealing descriptions for search results by highlighting the most important elements and key takeaways.
Optimize H1 tags
Every page on a website, including the homepage, needs to have one H1 tag. Ensure you only have one per page. The H1 tag is typically found at the top of the page and carries the most weight of all the subheading tags.
Optimize ALT Tags
The ALT text is used to describe an image to users who are visually impaired and also to search engines. Image optimization has become a very important factor of on-page SEO as it offers an additional opportunity to rank in search results. But don’t take this as an opportunity to keyword stuff, as it can hurt your ranking and be a hindrance to visually impaired users. Stick with natural language to describe your image.
Improve Relevancy: Term Frequency & LSI
LSI stands for latent semantic indexing and is used to help search engines process language and understand what a web page is about.
LSI keywords help search engines figure out the main topic of your article. As an example, if the topic of an article is “Spiders” and you have the words “legs”, “scary”, “arachnid” and so forth, these words let search engines know the page is talking about the animal.
However, if the content had other words such as “Google”, “web page”, “internet” then the search engine would know the page is about Google’s internet bots. These keywords send the right signals to search engines about the topic of each page. Using LSI, systems can rank documents based on their relevance to a topic.
What determines the weight of an LSI keyword?
How long is the field? The shorter the field, the higher the weight. If a term appears in a short field, such as a title field, it is more likely that the content of that field is about the term than if the same term appears in a much larger field.
Although using LSI keywords is gaining traction, it’s important that you use LSI keywords with your typical keywords and the other on-page SEO practices described in this article. LSI keywords are a ranking factor, however, they are one of many.
What is Tf*idf?
This brings us to TF*IDF, where Tf stands for Term Frequency and IDF stands for inverse document frequency. To break it down:
Term Frequency
How often does the term appear in this document?
The more often, the higher the weight given to the web page.
Inverse Document Frequency
How often does the term appear in all documents in the collection?
The more often, the lower the weight.
The Tf*idf equation can be expanded to include other variables, but these two lay the foundation of what search engines calculate to rank your page.
Why is this important for SEO?
These factors are how Google is scoring your pages on keywords related to your content. By filling out this equation, you can give a relevance score to your content. Then, using TF*idf tools, you can compare your scores to the scores of top-performing pages for any term.
Featured Snippets

A featured snippet is a block that shows up before the organic search results, describing the exact answer to a user’s query. The featured snippet is also called position 0 because it is shown above the top ranking spots.
Google picks the best answer to a query from third-party sites and features it in a snippet. Because featured snippets provide answers at a glance, they make the online search easier for users.
Why is ranking for a featured snippet important?
Customers who want their needs satisfied quickly rely on featured snippets for their information. The more you can satisfy their immediate needs, the more likely they are to click on your website and also develop positive feelings for your brand.
And this positive behavior has been observed. Ahrefs studied 2 million featured snippets and found that snippets will always get more traffic than the first organic search result.
How do I get ranked for a featured snippet?
Keyword research is a powerful tool for ranking in a featured snippet. Make sure to answer the questions your target audience is asking. Your content should be useful, straightforward, and offer users a valuable experience.
Keep in mind that most featured snippets have 40-50 words. One way to have your answers optimized for the featured snippet is through a Q&A page or section on your website. Answer the questions that people in your industry commonly ask. You can find these in the “People also ask” section in the search results.
Interlinking
Interlinking is the process of building an internal link structure on your website. The goal is to open pathways to the vital pages on your website to Google’s crawlers. Without proper interlinking, Google’s spiders are unable to crawl and understand your site.
With interlinking, Google can better understand the relationship between your pages, posts, and other content. What’s more, link value can be shared across all pages on your site.
For example, the homepage often has the greatest link value because it has the most backlinks. With interlinking, this value can be shared with all the links on the homepage, then passed to the links on those pages, and so on.
Why is interlinking important?
Besides being helpful for Google, interlinking can help users as well. A proper internal linking structure improves navigation for users and provides more ways to interact with a site.
Using anchor text keywords can aid users with their intent. Internal links keep users on sites longer, reducing the bounce rate while increasing the average visitor session. The longer a user stays on a site, the more likely they will complete a conversion.
Interlinking also helps newer pages you add to a site. If you publish a new blog post, it has no authority on its own. But with a link to the homepage or another key page, the link value will spread and help the new article be picked up by crawlers.
How do I set up internal links on my website?
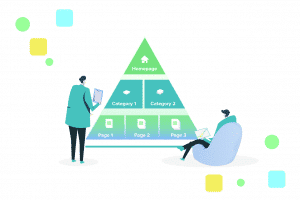
Pyramid Structure
A pyramid structure is the recommended approach to internal linking. Everything starts from the home page, then spreads to cornerstone pages which are key pages you want to rank for, before flowing to more pages. The goal is to have the fewest amount of links possible between any given page and the home page. This structure allows for link value to spread to the entire site, increasing the potential ranking and traffic of each page.
Anchor Text
Optimize all anchor text on your site to reflect the topic of the page you are linking. Placing irrelevant anchor text on a link will mark a website as spam.
Also, be sure to create keyword variations for your anchor text. Using the same anchor text for each link could qualify as spam. Particularly if you use the same anchor text on different pages, they will compete against each other and ruin your chances of ranking well.
Indexing: Making Sure Crawlers Search Your Relevant Pages

None of the optimization methods we mentioned above matter if the spiders don’t crawl your pages in the first place.
Indexing is the process by which Google and other search engines organize pages on their database, to be picked up when a user inputs a query. Without indexing, your site will not be added to the database or shown to users.
How do I know if my site is being indexed?
A quick way to check if your page is being indexed by Google is to search “site: YourDomainName” in a Google search. This will give you a rough view of which pages have been indexed by Google. You can also enter a specific page URL to see if it has been indexed.
How do I get Google to index my site?
There are quite a few methods you can use to have Google index your site, many of which have been mentioned in this article. The first method to note is that sites that update their content regularly are crawled more often. As well, having a good interlinking structure set up will allow Google’s spiders to crawl all of your relevant pages. Finally, image optimization is important and allows Google to gather more information from a site, even from images that it cannot see.
Submit a sitemap to Google
Sitemaps provide search engines with a list of the pages on your website. With a sitemap, even new content that does not have many links to it yet can be found by search engine bots.
Edit Robots.txt to stop Google from crawling irrelevant pages
Another method is to only let Google index vital parts of a website. There is no point in letting search engine bots crawl pages such as login pages and backend folders. Simply edit Robots.txt to exclude these pages and help Google only see the pages you wish to rank.
Keeping Up With On-Page SEO Best Practices
With these tips, you are well on your way to ranking in top positions on Google and getting the traffic necessary for your goals. However, remember that SEO is not a set it and forget it practice. On-page SEO needs to be continuously optimized and updated for the best results. Contact us today and see how we can optimize your on-page SEO elements for more conversions.