Apps enhance and expand the character of a user’s life at all times. As many mHealth apps grow, so do many HIPAA compliant mobile app development providers. Creating a healthcare app that interacts with electronically protected health information (ePHI), such as a hospital or health industry, will make you think about HIPAA.
HIPAA certification is generally geared toward medical devices, but it also applies to businesses like online pharmacies. HIPAA legislation does not address privacy restrictions for medical devices. However, developers should not disregard them.
What is HIPAA act?
In 1996, a law called the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) changed the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) and Public Health Service Act (PHSA).
HIPAA was designed to safeguard people who have health insurance and establish rules for storing and protecting personal medical information.
App developers’ HIPAA compliance checklist for mHealth apps
Unlike other health care reform laws, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act lacks any recommendations or best practices on how to employ specific techniques for encrypting patient data, for example. HIPAA and COVID, on the other hand, has a lot of implications for healthcare app developers.
As I mentioned, the HIPAA law has not changed since 2013. How do you think it’s managed to stay so popular for so long? Yes, I’m attempting to be as inclusive as possible.
That is all HIPAA has to say about the subject. Does it make your life easier by showing you how to make a HIPAA compliant email or a HIPAA compliant mobile app? “What constitutes an emergency?” “How should we build up emergency access procedures?” “Do I need to give authorized staff access to the healthcare app through a backdoor?” “How is this different from authorized persons accessing patient data in non-emergency situations?” I’m sure it brings up many questions.
Let me provide you with some practical advice by summarizing the most actionable HIPAA guidelines that you should follow during the creation of your health app:
Minimize the amount of data
Make sure you’re just gathering information that will help your app function better and be more beneficial to your patients. We also advise against caching PHI and keeping track of users’ geolocation data (other than state-level).
Secure connection and protocols are used to transfer PHI
To keep patient data resistant to intrusions, you must encrypt it and transport it over a secure HTTPS connection with SSL/TLS. Simply ensure that your app developers are using these technologies while creating HIPAA compliant software.
Include an audit mechanism in the process
It should be possible to see who is using the app and what actions they are taking. Basically, audit controls such as these require specific user identification.
PHI must be removed from notifications and emails
It’s vital to note that PHI received via push notifications and emails on mobile devices can be easily compromised. Text messaging, like practically all other non-app messaging, is in the same boat.
Ensure the accuracy of your information
Unauthorized modifications to PHI should be impossible. When it comes to maintaining patient data integrity, blockchain technology is truly invaluable. Consider transferring EHR (electronic health records) to a blockchain to create HIPAA compliant, hack-resistant software.
Why should you follow this HIPAA compliance?
HIPAA is arguably most beneficial to patients. HIPAA is significant because it mandates that healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and HIPAA-covered businesses’ business connections establish several protections to secure sensitive personal and health information.
While no healthcare organization wants sensitive data or health information to be exposed or stolen, healthcare firms have no duty to preserve data – and no consequences if they do not.
HIPAA established laws requiring healthcare institutions to regulate who has access to health data, limiting who may view health information and who can share it. HIPAA rights ensure that any information supplied to healthcare providers and health plans and information created, transmitted, or held by them is subject to stringent security safeguards. Patients also have discretion over who receives and shares their information.
HIPAA form is essential for patients who wish to be more involved in their healthcare and acquire copies of their medical records. Healthcare companies can make mistakes when recording health information, even if they take great care. If patients can access copies, they will be able to check for problems and ensure that they are fixed.
What do HIPAA compliance requirements entail?
HIPAA compliant software comprises following HIPAA’s requirements and any related HIPAA minimum rule, amendment, or regulation. It is both stringent (with a slew of rules and harsh punishments) and ambiguous (with liberty on how best to apply the rules).
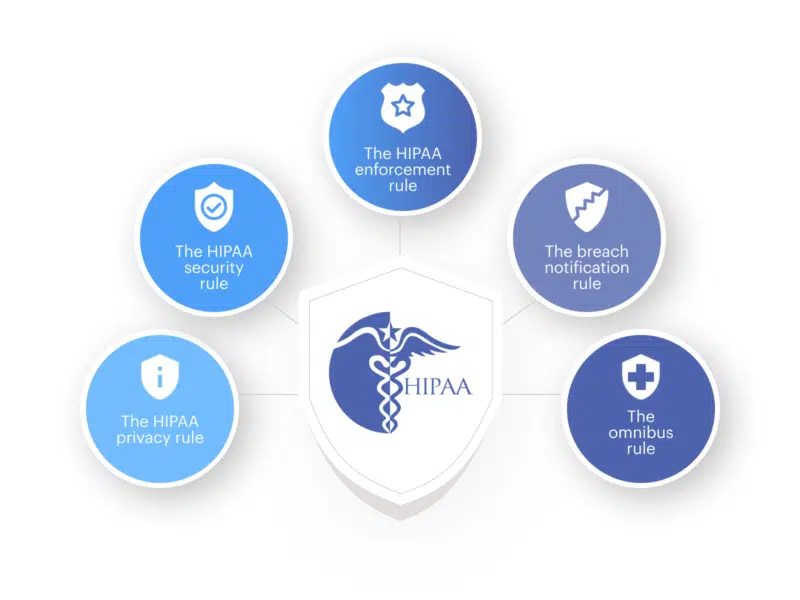
HIPAA forms five fundamental guidelines that all healthcare software development applications must follow:
1. The HIPAA privacy rule
Privacy Rule establishes protections for the use and disclosure of medical records and other protected health information (PHI). The rule is intended to make the transfer of health data more efficient while also reducing fraud and theft. Patients also have specific rights to their health information and medical records under the rule, including the ability to examine, receive a copy, and request adjustments to their data.
2. The HIPAA security rule
Security Rule aims to protect ePHI created, received, used, and maintained by covered entities. According to the Security Rule, covered entities must implement “necessary administrative, physical, and technical protections to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security” of ePHI. Although HIPAA may not usually specify minimal or exact standards, the NIST guide on HIPAA implementation is frequently cited.
3. The HIPAA enforcement rule
The Enforcement Rule lays out how the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) would enforce HIPAA, with regulators determining culpability and imposing fines for noncompliance. A complaint or a data breach normally triggers an investigation, but the Department of Health and Human Services can investigate for no cause.
4. The breach notification rule
The Breach Notification Rule requires HIPAA-covered entities and their business partners to notify HIPAA-covered entities and their business associates of any unsecured PHI breach, including both paper-based and electronic PHI. The nature and extent of the PHI implicated, the type of disclosure, whether the data was accessed, and the level of risk of exposure are all factors that HHS considers when determining what constitutes a breach. Breach notifications that affect more than 500 people must include a media announcement and other procedures.
5. The omnibus rule
HIPAA’s Omnibus Rule, modified in 2013 and affecting several HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Enforcement Rules, is the most recent amendment. This Rule is stricter, making it more difficult to dodge breach notification, expanding non-compliance liabilities to business affiliates, and imposing new privacy limits for PHI use.
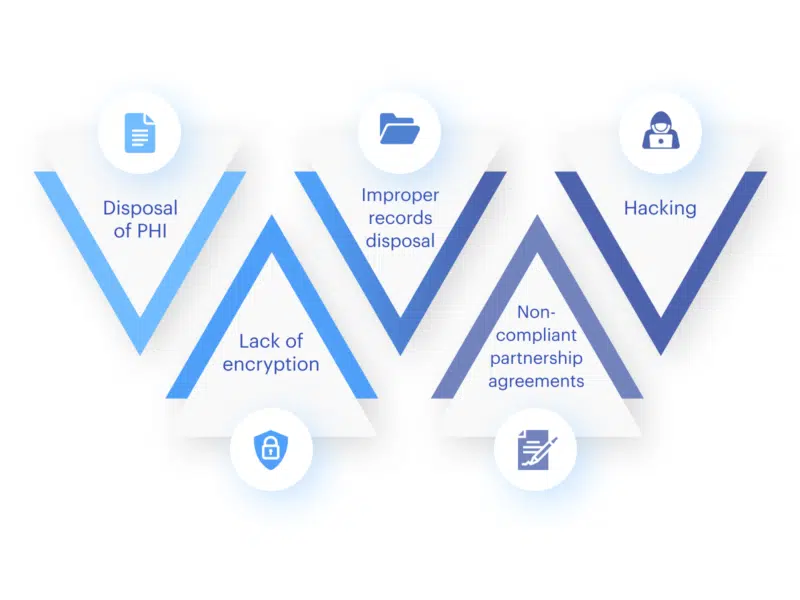
The most common HIPAA violations
1. Disposal of PHI
It is critical that your personnel appropriately dispose of any unnecessary PHI information.
This is true for both physical and digital documents. If someone leaves a document on a table or leaves patient information on their desktop, it could end up in the hands of the wrong people (and hence, resulting in a HIPAA violation).
The recommended approach here is to either retain the information in a secure location or delete/shred it if the paper itself is no longer useful.
2. Lack of encryption
Encrypting your PHI will prevent it from falling into the wrong hands.
Even if there is a breach and PHI data is stolen, hackers won’t be able to access it without the private key, which adds an extra layer of security on top of all the other best practices.
Furthermore, hospital personnel should use encrypted communications applications. True, texting is a convenient way to communicate. There’s a danger that the SMS will be intercepted by hostile cybercriminals unless they’re sent through encrypted software.
3. Improper records disposal
At first look, records disposal appears to be an unusual reason for so many HIPAA violations. Staff may, however, make the error of assuming that documents do not include PHI. Carelessly discarding these documents results in a breach.
PHI may remain on hard drives and USB drives until deleted or destroyed, for example. Unless they are accounted for and stored under lock and key between the time they are used and the time they are wiped of PHI, they may constitute or lead to a violation.
You need strong and unambiguous regulations on document and device handling to secure your company. In this area, you should also train your team on acceptable procedures and any HIPAA violation.
4. Non-compliant partnership agreements
HIPAA violations involving non-compliant partnership agreements are simple and widespread. In its daily activities, the ordinary healthcare organization collaborates with a variety of partners. The potential for difficulties appears to be limitless.
To handle urgent facility needs, partners need to brought on board immediately.
Regional or off-site departments may be in charge of contracts.
A business can acquire, trade, or merge with its partners.
It’s possible for errors or misconceptions to lead to non-compliant agreements in these and other situations. However, the costs of these mistakes can be high. The best way to secure your business is to ensure that those in charge of partner contracts have received proper HIPAA training.
5. Hacking
Hacking is a genuine threat to medical ePHI, despite our best efforts to believe it won’t happen to us. Because there are people out there who want to use this information for bad purposes, medical practices should take precautions to protect themselves from hackers.
Antivirus software that is up to current and active on all devices that hold ePHI is a good place to start. Firewalls provide an additional degree of security. Finally, another vital action to take to prevent hacking is to create unique and difficult-to-remember passwords and change them periodically.
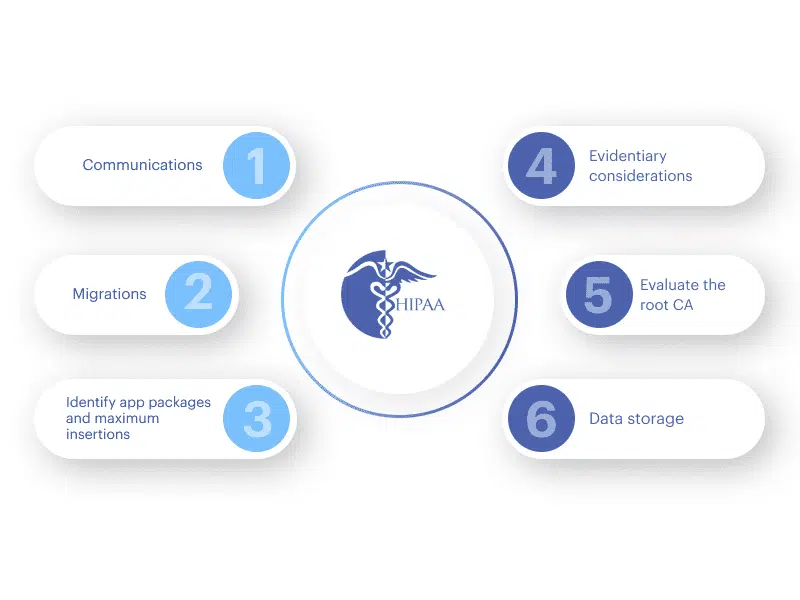
How to create a HIPAA compliance mobile app
HIPAA protects health information by requiring healthcare apps to meet certain minimal data security requirements throughout creation. These recommendations should followed by any healthcare mobile app development company that has to bring the app into production. This regulated activity preserves the confidentiality of a patient’s vital health information.
Following a data breach, every user’s data poses a health and safety risk. HIPAA requires businesses to adhere to the following rules:
1. Communications
You should include an emergency call-to-action button on your app/website so users can contact you even if their normal phone is out of service. Make sure that you automatically publish any material generated by users on your website to your app as well. To include material, the user does not have to understand or engage with it.
Make sure your app can upload and download data without jeopardizing the security or integrity of your data. It’s also a good idea to make sure that your app exclusively uses HTTPS to connect with the server and access secure HTTP resources. Access to concealed media is impossible without express user consent. Hide any content – photos, video, or audio – is explicitly linked to full user consent and can be considered an EOI.
2. Migrations
The first and most serious HIPAA risk is migrating the existing website platform in-house. Its danger increases dramatically if a healthcare practitioner uses a website platform established by a third-party vendor, such as Manta, Joomla, or WordPress, which the healthcare practitioner continues to use.
Consider the possibility that your doctor is already using or developing applications. In that scenario, consider your alternatives for designing an app and do an in-person interview with the healthcare provider to learn more about how it could benefit them. You may have access to this type of data as part of your HIPAA compliance procedure, depending on the platform the healthcare practitioner is currently using.
3. Identify app packages and maximum insertions
The first stage is to figure out what an app’s basic functionality is or how much data the programmer will provide. You can assess this based on the app’s purpose, such as if it is a key contact lab or a corporate therapeutic solution.
A thorough examination of the app’s sheer size indicates the possibility of data security vulnerabilities. Outsourcing or outsourcing health app developers ensure that all technical standards met during the development process. Otherwise, the app’s life cycle will stretched. Furthermore, there must be no unnecessary bulk data; some contemporary apps may have five times or more than the required data.
4. Evidentiary considerations
A HIPAA app’s main goal is to help you run a more efficient healthcare routine. As a result, all of the app’s operations must be based on the principle of safety. Data must first be collected before the apps can be used. The underpinning software should be able to encapsulate data feeds from online sources.
Data from third-party data sources should not be saved in a format that leaves gaps in time, such as a week. Finally, because HIPAA does not require the use of encryption technologies in apps, encryption should emphasized. It is important that encryption technology is safe, secure, and available from one central location.
5. Evaluate the root CA
Finally, it’s vital to review the development team’s infrastructure in order to retain this critical security measure. For example, there could be a hidden connection to the app’s owner, or a single person could set up a rogue server to keep important information.
It might be prudent to discuss this idea with the development team. Implementing business security solutions that help anticipate and prevent unauthorized access to data hosted on AWS can help reduce the likelihood of unauthorized third parties developing a rogue CA infrastructure for storing healthcare data.
6. Data storage
Sensitive data contained within the app is one of the most critical aspects. Blocked ports, wireless setups, or handwritten app contents will not protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Keeping these critical files in a safe, centralized location with failover capability is vital.
How to prevent HIPAA violations?
HIPAA infractions may be terrifying for any company. There are, however, steps you can take to avoid HIPAA violation fines and reduce your company’s risk of falling out of compliance with HIPAA bridge rule.
Proper HIPAA training is one of the best methods to avoid potential data breaches. Annual or bi-annual HIPAA compliant training is an excellent way to keep your team informed about new policies and practices.
Another simple strategy to avoid HIPAA issues for any employees that handle PHI is to:
- It is not advisable to post ePHI to social media
- Never send PHI-containing SMS text messages.
- Create policies that only allow necessary employees access to the facility.
- Encrypt your data.
- Report HIPAA violation.
FAQs
1. What does HIPAA stand for?
The term HIPAA stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, also widely used to refer to the numerous regulations that have been issued under that law since its passage.
2. Who enforces HIPAA?
The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) of the Department of Health and Human Services is primarily enforcing HIPAA Rules.
3. Who does HIPAA apply to?
The HIPAA minimum necessary standard applies to Most employers who sponsor or co-sponsor employee health insurance plans, most health insurance companies, and most workers. HIPAA, on the other hand, consists of four more titles addressing anything from taxes on expatriates who renounce U.S. citizenship to medical liability reform.
Conclusion
We are rapidly entering an era where digital healthcare transformation will be the new standard due to the impact of the Coronavirus outbreak in the healthcare sector. It implies that there will be a significant shift in emphasis in the future toward compliance adherence. The most successful healthcare digital transformationists will be those who master the complexities of compliance and apply them to their medical software today.
If you’re looking for a technical partner to help you bootstrap with healthcare app development services, Markovate’s experienced team of designers and developers can consult, build, and execute your next transformative notion.