Android vs iOS Security: Introduction
Android vs iOS security, which is the most secure for your enterprise’s app?
Worldwide spending on cybersecurity is forecasted to reach $133.7 billion in 2022. This alarming statistic shows people’s importance in protecting users’ data and avoiding cyber crimes. There is a certain level of trust when blindly entering our data on many apps or websites. Applications require data to store information for further uses, giving accurate real-time insights and significantly increasing the app’s functionality.
But, when hackers compromise a user’s security, they use applications as a medium to hack their data and use it maliciously for personal gain. App developers evidently give utmost importance to app security when developing apps. Along with the other app features such as APIs, design, and third-party plugins, the team sometimes does overlook the cybersecurity aspect. This leads to security threats and degrades the app’s performance and user experience significantly.
An average of 24,000 malicious mobile apps are blocked daily on the internet. Specific steps and measures have been taken to prevent this from happening and protect the app from digital malware, which can lead to any cyber attack.
This article will discuss the two security characteristics of the biggest platforms in the app development industry, Android vs iOS security.
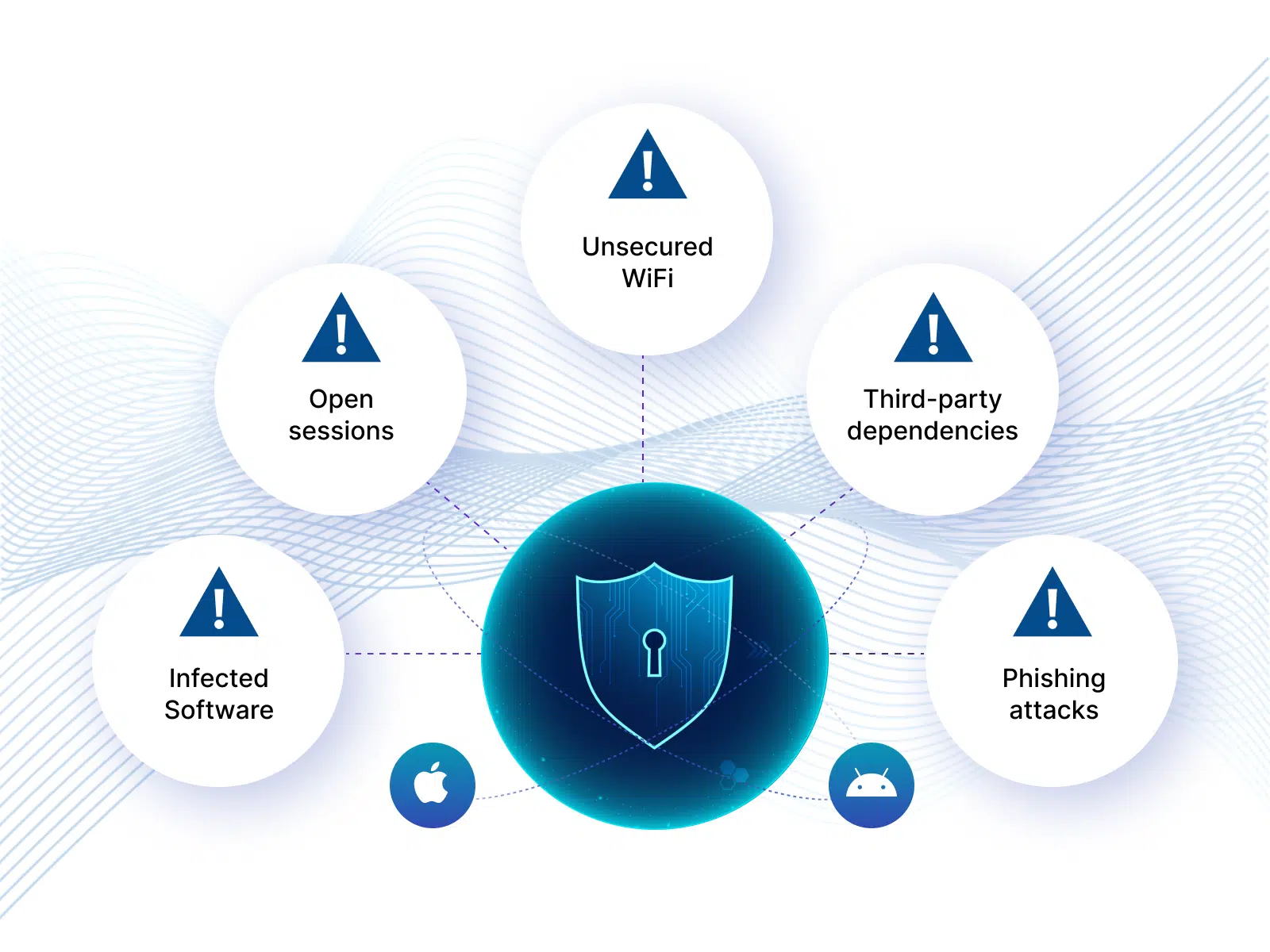
Android vs iOS Security: Possible Security Threats For Apps
When talking about Android vs iOS security, various possible mobile security threats could weaken your app and result in data breaches:
1. Infected Software
Malware-infected apps are one of the most common reasons for security threats. Most of the time, we download software and give permissions without going into too much detail. Sometimes, criminals hack these and inject corrupted files into them under the pretense of helpful software.
Thus, when unsuspecting users use this software, it might be in the form of valuable tools such as pdf converters or image-editing software. The criminal can steal their information, plant some virus or unknowingly sign you up for unauthorized activities.
2. Open Sessions
Improper session handling mainly occurs when the user enters their details for authentication and the system generates a session token. Apps do this to ensure a smooth transaction between the client and the server. The authentication, when approved by the backend, generates the session token.
Thus, anyone with access to these tokens can falsely impersonate the user and use these details to gain access to various services. Therefore, if sessions are left open, for instance, when you do not log out or are mishandled, these can result in fraud and information theft.
3. Unsecured WiFi
There are a lot of times when users connect to free public networks which do not require any password, such as in airports, small areas, etc. This avoids burning your phone through cellular data or personal hotspots. However, when using a public network, you do not have any control over its security and data encryption.
Maybe then, if you log into a website, other users in this network might see what you’re accessing and all the details you are entering, which they could use for harmful purposes. Therefore, accessing financial information, private photos, and important documents is not advisable if you are in a public place and using their WiFi.
4. Through Third-Party Dependencies
Security threats might also arise from the app’s third-party libraries to add more features and better the user experience. Apps utilize multiple libraries, scripts, and plugins imported from an external source. These might contain some vulnerabilities unknown to the developer and can later harm the app.
In addition, third-party dependencies generally focus on functionality and do not come with a high-security layer, making it an exposed point of attack for hackers. This can affect the app’s performance, compromise the user’s information and give unauthorized access to other systems.
5. Phishing Attacks
These attacks are quite common and dangerous, where the hacker poses as a trusted entity and sends the user a link that might appear helpful but would harm the system.
These attacks are usually in the form of spam mail and fraud messages to lure the user, under a false identity, to click on them. On interacting with these links, the recipient might have consequences, such as malware installation, errors in system software, etc.
Android vs iOS Security: The Threat Level
Both platforms employ various safety measures to prevent these security threats:
Android
- Their open-source code makes it easier to find bugs and debug them with the help of community support.
- It offers multiple security settings which help you customize your privacy needs as per your choice.
- Due to its broad customer base and security, it receives more feedback, and developers detect and solve more problems.
- Android provides an Android Enterprise Essentials management service that offers critical security features and helps your app to become malware-resistant.
iOS
- Apple has a closed source code, which makes any modifications extremely tough, and thus minimizes the scope for vulnerabilities.
- iOS devices are continuously updated, and all devices contain the latest security measures by default. Apple puts a lot of effort into protecting the user’s data and privacy.
- These are consistent and reliable by themselves, and the user does not have to worry much about customizing their settings or unlocking hidden features to increase their app security.
- Unlike Android, where anybody publishes apps, the App store requires extensive testing and scrutiny. This ensures that Apple has a close watch on the apps and the performance they are offering.
Android vs iOS Security: Which Is Safer For Apps & Why?
There is a security risk on both platforms since the user’s crucial information, if obtained by the hacker, can be hugely profitable for them, and they would go to any lengths to extract it.
But when comparing iPhone security vs. Android, iOS is considered safer for apps, considering the tight security and checks Apple performs before putting apps up on the Appstore. It’s more challenging for hackers to find loopholes in iOS devices as it’s a closed-sourced system, and the developers cannot easily modify the code.
Apple focuses a lot on data security, and the user’s privacy is one of its top priorities.
Also, users worldwide widely use Android, with developers making multiple modifications and customizations to suit their customer bases. This makes it more prone to attacks and might override security features.
Android vs iOS – A quick comparison
| Criteria | Android | iOS | Analysis & Why It Matters |
| Source Code Availability | Open Source | Closed Source | Android’s open-source nature allows for greater scrutiny but also exposes it to more potential vulnerabilities. iOS’s closed-source approach is less transparent but often considered more secure. |
| App Store Policies | Less Stringent | Stringent | Apple’s App Store has stricter review policies, which generally leads to safer apps. Google Play Store is easier to enter, increasing the risk of malicious apps. |
| User Permissions | Granular, can be confusing | Simplified, easier to manage | Android allows for more granular permissions, but this can confuse users into granting unnecessary permissions. iOS’s permissions are simpler and generally more user-friendly, which can lead to safer choices. |
| OS Updates | Fragmented, depends on manufacturer | Uniform, controlled by Apple | Apple provides regular security updates directly. Manufacturers or carriers may delay Android updates, leaving some devices vulnerable. |
| Built-in Security Features | Secure Boot, Device Encryption, Google Play Protect | Secure Enclave, FaceID, TouchID, end-to-end encryption | Both platforms have robust built-in security features, but iOS’s are generally considered more tightly integrated due to Apple’s control over hardware and software. |
| Third-Party Security Apps | More options available | Limited due to iOS restrictions | Android users have more options for third-party security apps, but this is partly because iOS’s built-in security is often deemed sufficient. |
| Malware Vulnerability | Higher | Lower | Android’s open nature makes it a more attractive target for malware, whereas iOS’s walled garden approach minimizes risk. |
| Jailbreaking & Rooting | More common, easier | Less common, harder | Rooting Android devices is more straightforward, but it exposes the system to security risks. Jailbreaking an iPhone is harder and less common, preserving security at the expense of customizability. |
| Data Encryption | Available, but can vary | Strong, uniform encryption across devices | iOS prioritizes data encryption and makes it a standard feature. Android offers encryption but can be inconsistent depending on the device and manufacturer. |
| Enterprise Security | Android Enterprise, but often customized | Extensive MDM and enterprise solutions | iOS is often preferred in corporate settings due to its comprehensive Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions. Android Enterprise exists but may require customization. |
What security features do iOS and Android have in common?
In the world of smartphone security, iOS and Android share some key features. Both use a concept known as “sandboxing,” which essentially means that apps run in their own separate spaces to prevent harmful software from affecting the whole system.
When it comes to keeping your stored data safe, iOS automatically encrypts it. Android also offers this feature, but users must enable it themselves through their settings since it’s not turned on by default.
Finally, both operating systems support the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which protect your data when you’re connected to the internet. This is especially important for mobile devices that frequently connect to public Wi-Fi networks. Top providers like NordVPN offer strong security for both iOS and Android systems, even though not all VPN services are created equal.
Android vs iOS Security: Tips For Businesses
1. Do not compromise on security. Ensure that the hiring developers have a fair knowledge of app security and implement the necessary protocols to prevent cyber attacks.
2. The backend should be completely secure and not have any vulnerabilities, such as APIs. Cross-check if they are entirely verified for the platform you are developing your application since they conduct all the authentication and data transfer.
3. Emphasis on encryption and strong authentication. This will make hacking the application incredibly for the hacker. Encryption would help transfer the data over the server safely, without being visible to any external authority. In addition, authentication methods such as two-factor authentication would help to increase security.
4. Avoid storing private and sensitive information that might be utilized later. Increased app security threats can give hackers permanent access to user information stored on devices or servers.
5. Stay updated with the latest cryptographic technique and algorithms that help encrypt the data. This might help to throw the hacker off track and stay in touch with the latest security requirements.
6. Thoroughly do the testing and QA rounds. Manually test all app loopholes and bugs, and use white-hat hackers for safety before deployment.
Conclusion: Android vs iOS
Investing in app security and protecting the user’s data is essential. Black-hat hackers have boosted their use of servers and internet resources as cybercrime has reached an all-time high.
Both iOS and Android have their pros and cons when it comes to security measures. Thus, choosing the platform that suits your business needs and prioritizes the user’s data is essential. One must carefully consider when and where they enter critical information and review all the permissions granted to the program.
Further Read: How To Prevent Security Threats For Enterprise Application Development?
Android vs iOS Security: FAQs
1. What are some common mobile app security threats?
Some common mobile app security threats are phishing attacks, spyware, weak server-side controls, and app code vulnerabilities. The most common threat remains data leakage, which can be extremely dangerous for the user. However, certain practices can prevent these security threats to a large extent.
2. Why is app security important for businesses?
App security is essential for businesses, ensuring a smooth user experience, building loyalty, and fostering trust in the company. Today’s apps’ cloud connections can also increase security threats, posing risks to enterprises and businesses.