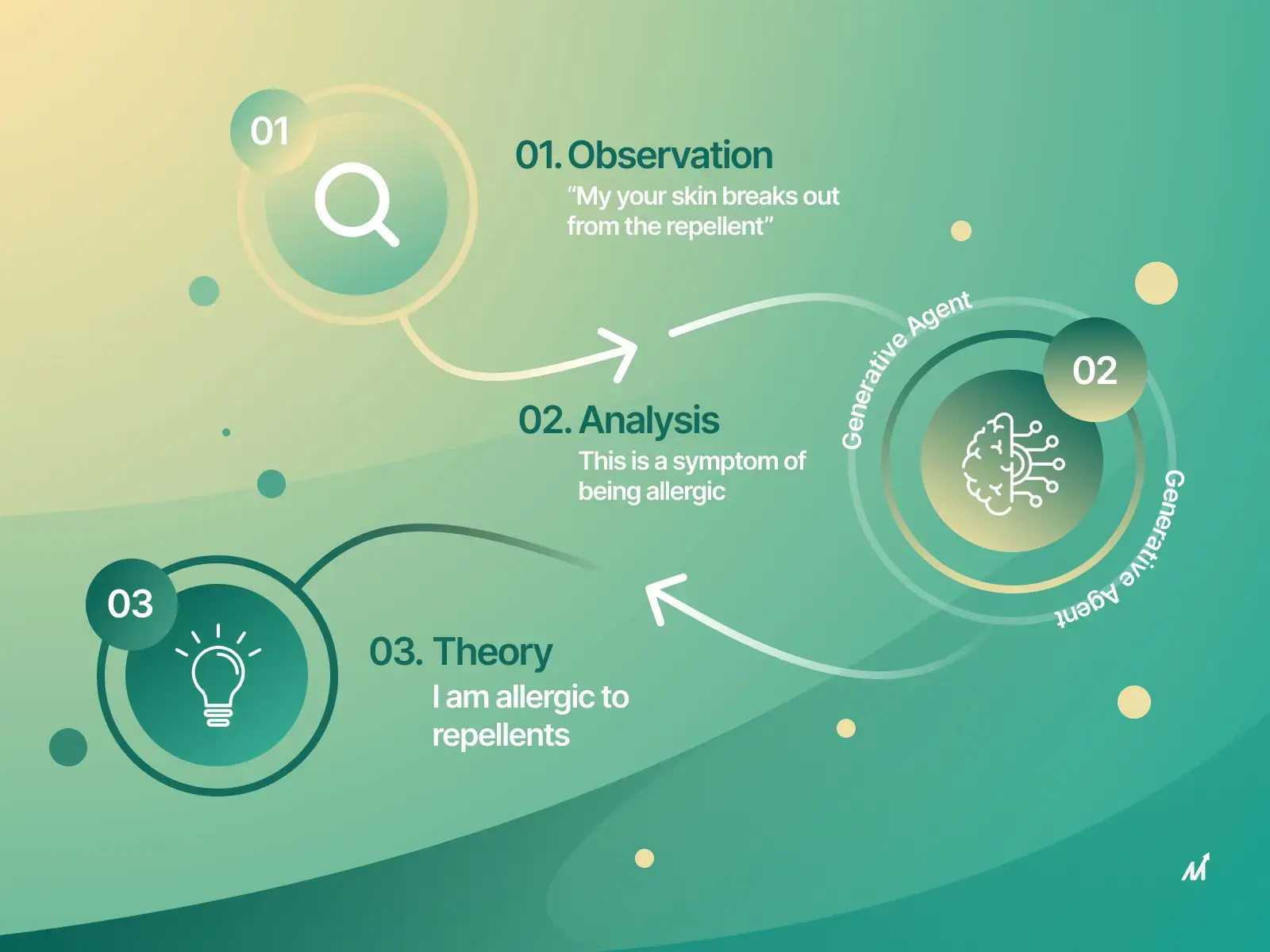
In the rapidly evolving landscape of business technology, AI agents stand out as a transformative force, particularly within enterprise environments. These sophisticated systems are powered by advanced algorithms and capable of semi-autonomous functions. AI agents are redefining traditional business processes, leading to significant enhancements in efficiency, decision-making, and customer engagement.
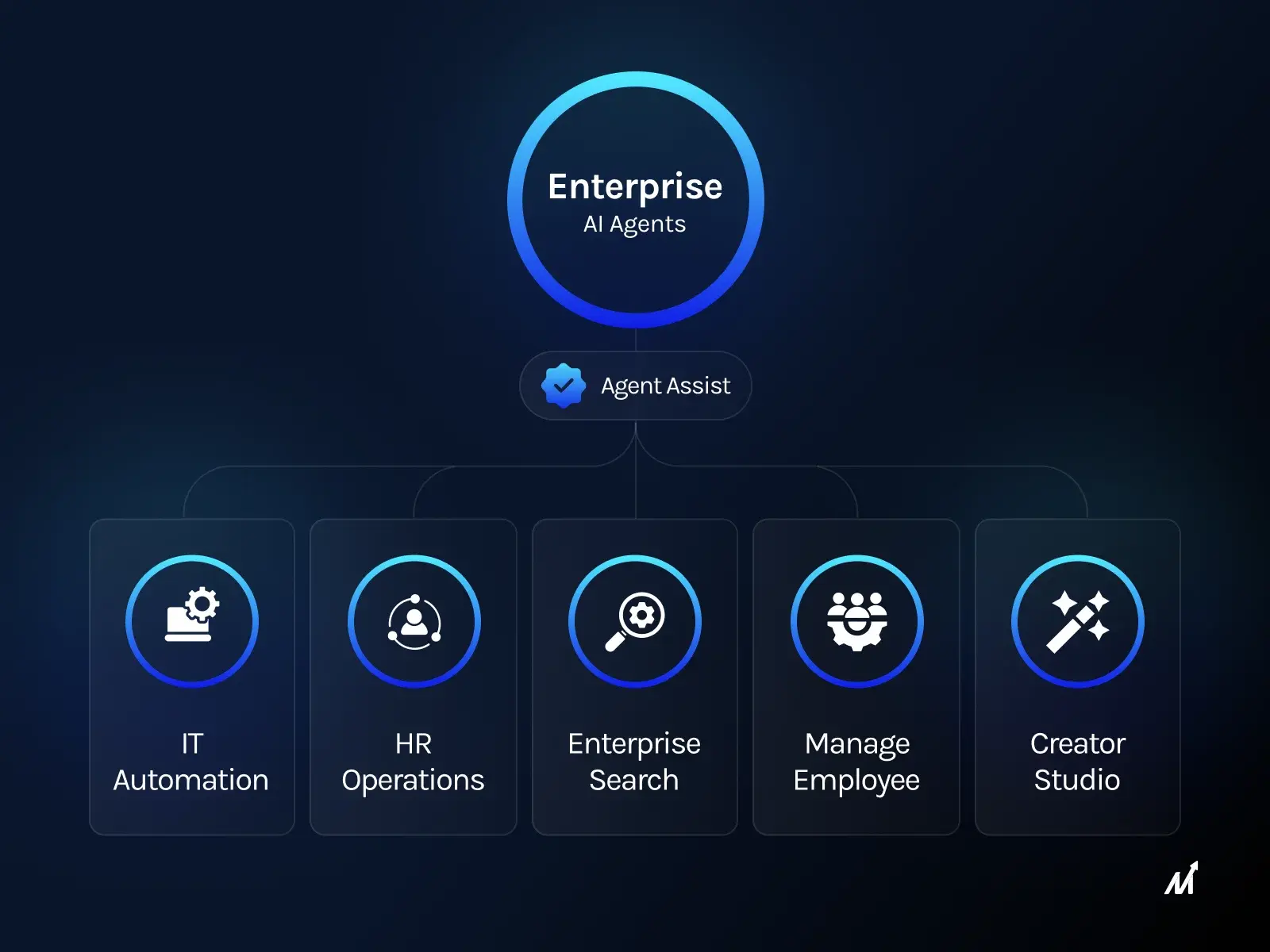
Understanding AI Agents and Enterprise AI Agents
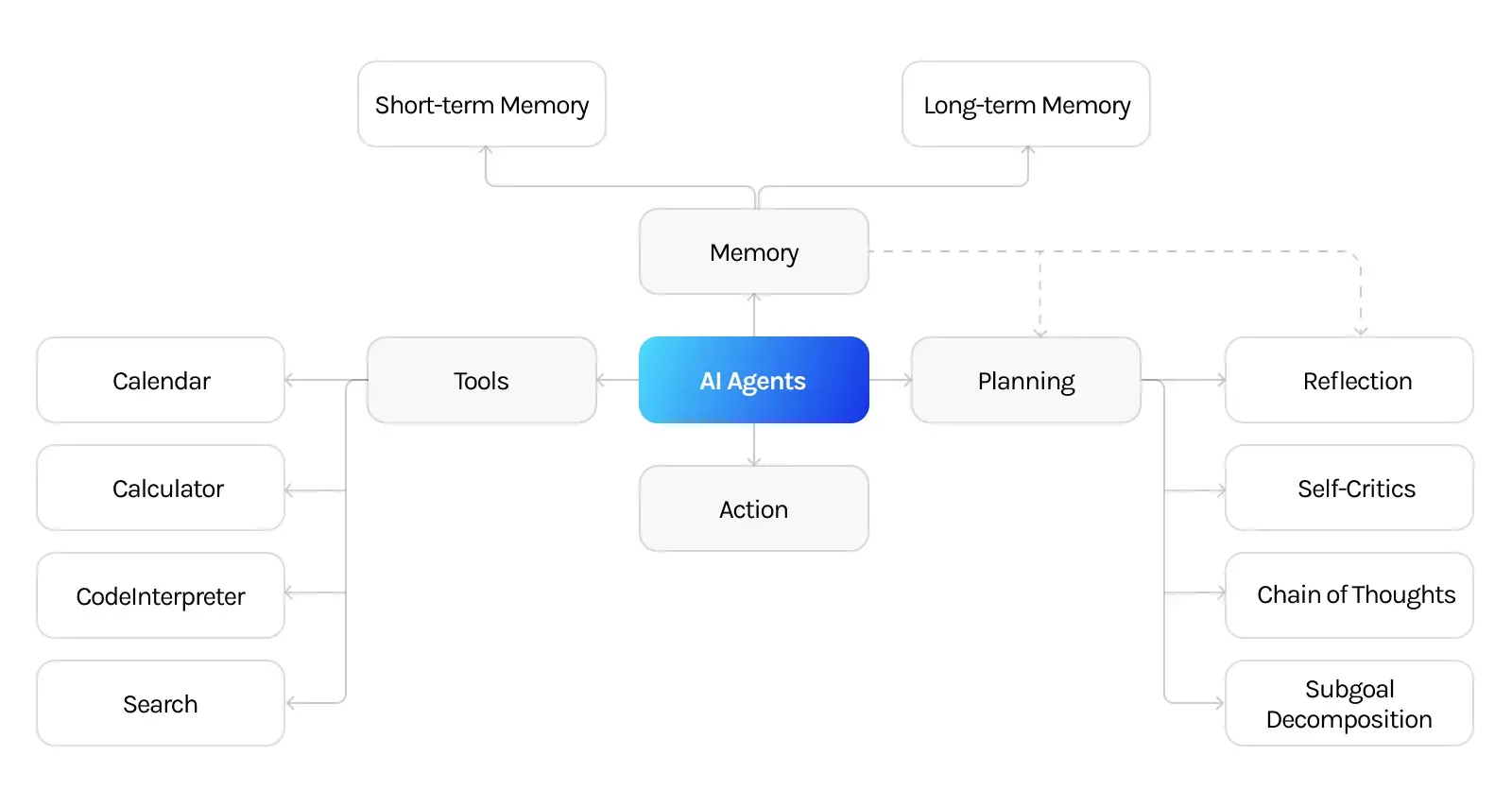
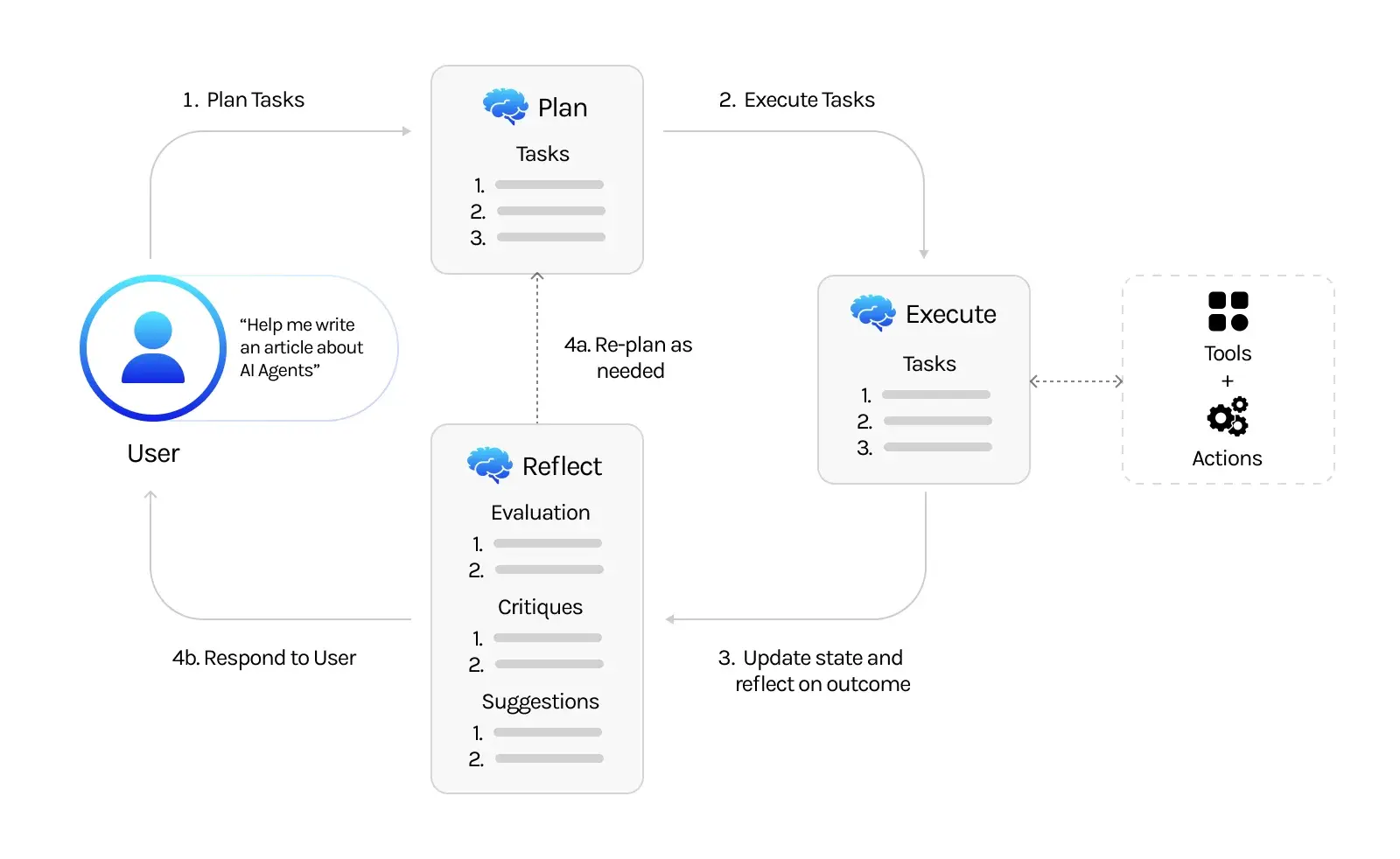
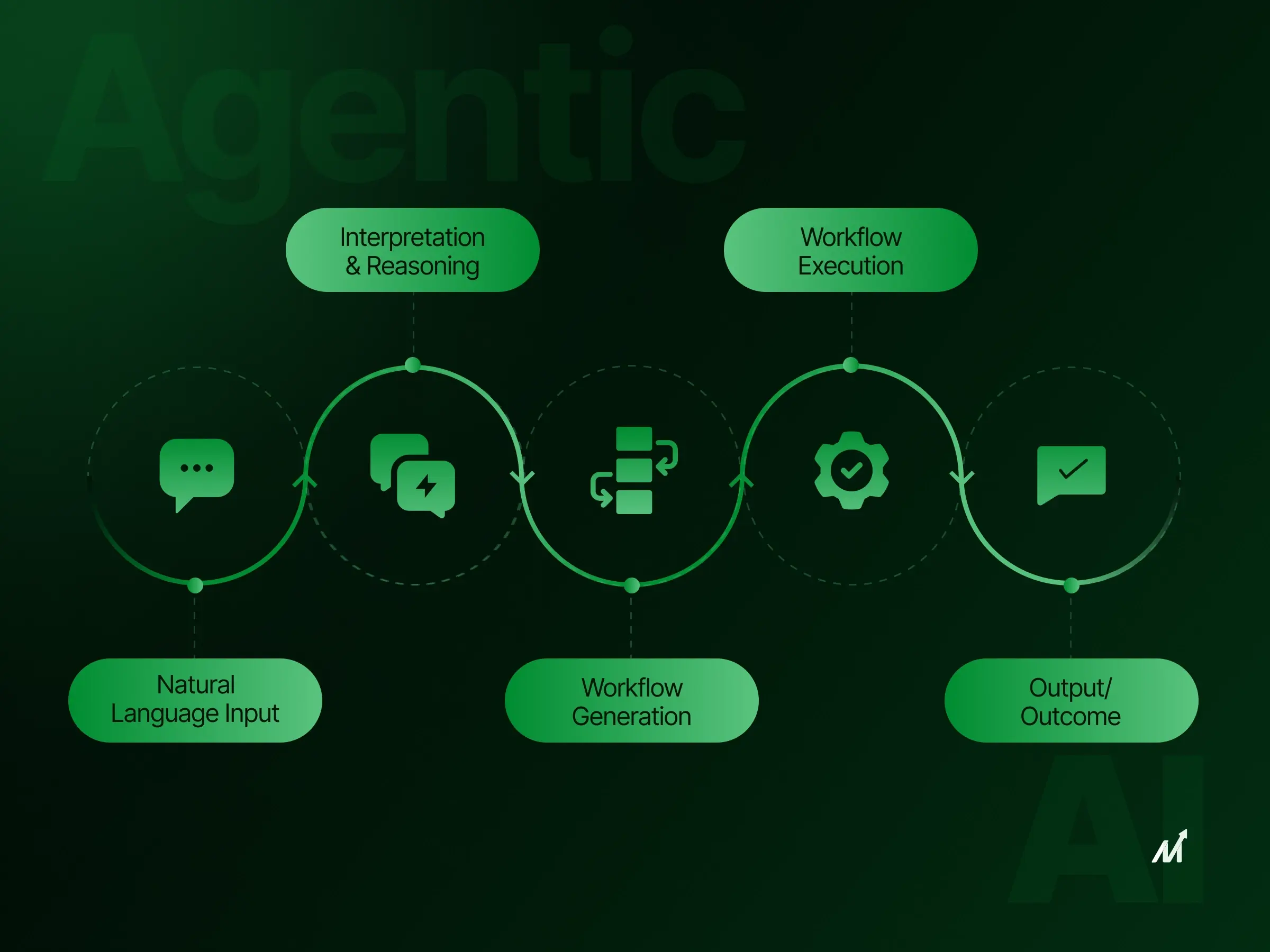
At its core, an AI agent is a system capable of observing its environment through sensors. It can then act upon that environment through actuators. In the context of business, these agents are embedded with algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data. The agents learn from these insights and make decisions or take actions autonomously. Enterprise AI agents are a specialized subset of AI agents tailored for complex business environments. They integrate deeply with enterprise systems, handling various complex tasks. These tasks can range from automated customer service to complex decision-making that aligns with business objectives.
Technical Foundation of Enterprise AI Agents
Enterprise AI agents are built on several technological pillars:
- Machine Learning (ML): At the heart of AI agents lies ML models that enable them to predict outcomes based on data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI agents use NLP to understand and generate human language. This capability makes them adept at tasks such as customer support and generating reports.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): This technology helps AI agents to perform repetitive tasks quickly and accurately.
- Cognitive Automation: This combines ML and RPA, enabling AI agents to handle higher-level decision-making and problem-solving.
Examples of Enterprise AI Agents in Action
- Customer Service: AI agents are employed to manage customer queries around the clock, providing immediate responses to common questions and escalating more complex issues to human agents. For example, a telecommunications company might use AI agents to handle thousands of routine customer interactions daily, freeing human employees to tackle more complex customer needs.
- Supply Chain Management: AI agents optimize supply chain operations by predicting inventory levels, managing restocking processes automatically, and identifying the fastest and most cost-effective shipping routes. A notable example is how major retailers use AI agents to manage their inventory across hundreds of stores nationwide, ensuring products are always available to meet consumer demand.
- Human Resources: AI agents streamline HR processes by automating candidate screening, scheduling interviews, and even conducting initial assessments. This not only speeds up the recruitment process but also helps reduce biases in candidate selection.
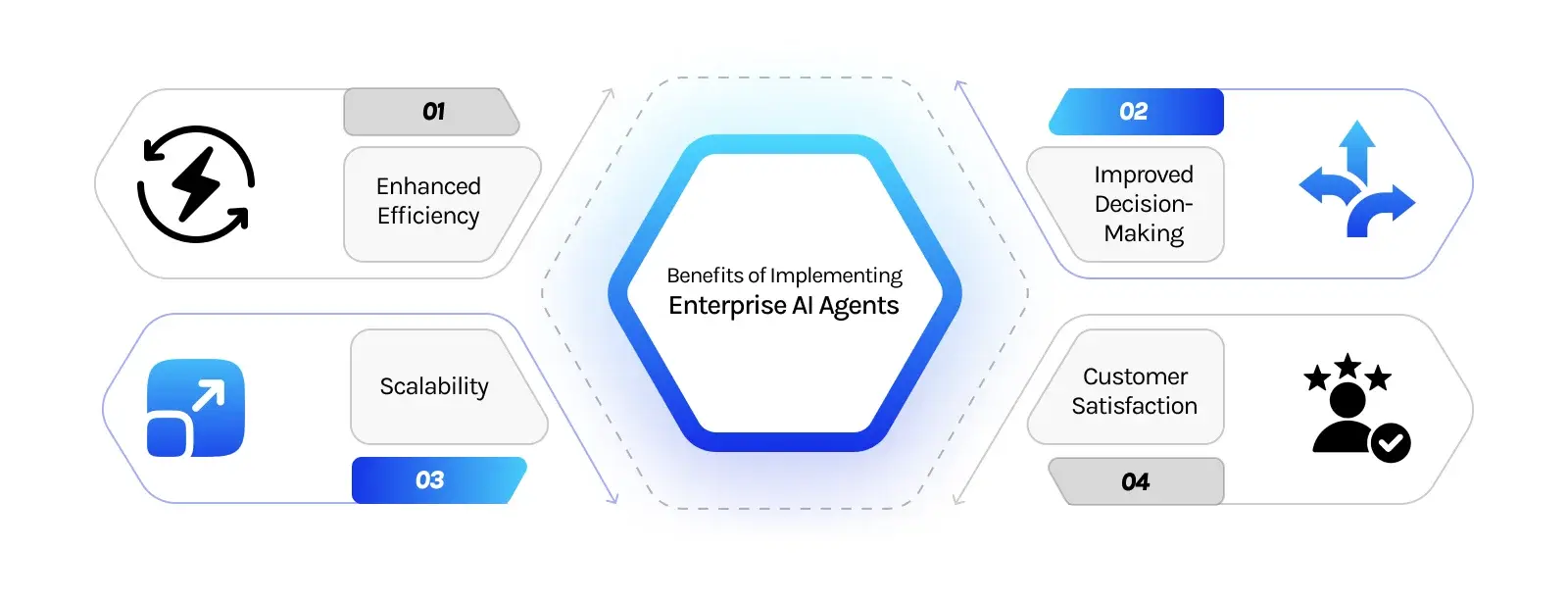
Benefits of Implementing Enterprise AI Agents
- Enhanced Efficiency: By automating routine tasks, AI agents free up human employees to focus on more strategic activities. This shift not only speeds up operations but also reduces human error and operational costs.
- Improved Decision-Making: With the ability to analyze large datasets quickly, AI agents provide insights that help businesses make informed decisions faster than ever before. This capability is crucial in environments where speed and accuracy are paramount, such as financial trading or emergency response planning.
- Scalability: AI agents can handle a growing number of tasks without the need for proportionate increases in human labor. This scalability is particularly beneficial for enterprises looking to expand operations without a significant increase in overhead.
- Customer Satisfaction: AI agents provide personalized customer interactions based on previous engagement history, enhancing the customer experience and increasing loyalty.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are significant, enterprises must also consider several challenges when implementing AI agents:
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AI agents with existing systems can be complex and requires careful planning and execution.
- Data Privacy and Security: Enterprises must ensure that AI agents operate in compliance with data protection regulations, as they often handle sensitive information.
- Ongoing Training and Maintenance: AI agents require continuous training and updates to adapt to changing business environments and maintain their effectiveness.
Conclusion
Enterprise AI agents are not just a technological upgrade; they represent a paradigm shift in how businesses operate. By automating routine tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving customer interactions, AI agents are set to redefine the landscape of enterprise operations. As more businesses recognize their potential, the adoption of AI agents is likely to accelerate, heralding a new era of business efficiency and innovation.
Need help building, integrating, or training AI agents for your business, contact our AI experts.